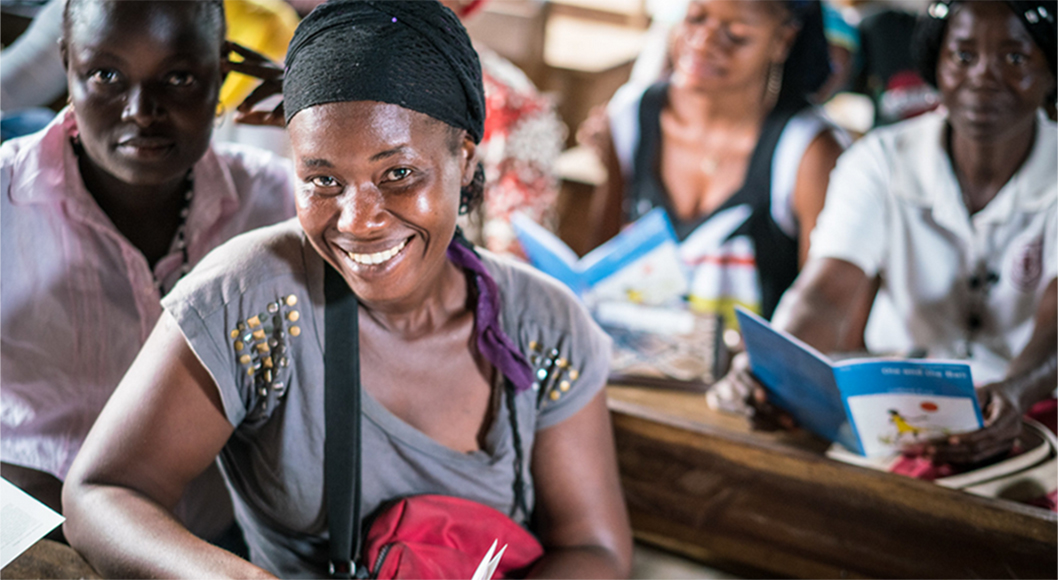
While significant gains in global health have been made over the past several decades, there is still much work to be done. Family planning and reproductive health services are of particular importance. According to the World Health Organization’s Fact Sheet No. 351, 222 million women in developing countries lack access to desired family planning services. To increase access to needed family planning services, as well as other key health services such as HIV&AIDS; maternal, newborn, and child health; nutrition; and control of infectious disease, building the capacity of local organizations is necessary. Through Advancing Partners & Communities’ grants mechanism and capacity building assistance, local NGOs were able to meet this need while receiving institutional strengthening assistance.
Advancing Partners & Communities (APC) was a seven-year USAID-funded project implemented by JSI Research & Training Institute (JSI) and partner FHI 360. It advanced and supported community programs that sought to improve the overall health of communities and achieve other health-related impacts, especially in relationship to family planning. APC provided global leadership for community-based programming, executed and managed small and medium-sized sub-awards, supported procurement reform by preparing awards for execution by USAID, and built technical capacity of organizations to implement effective programs.
APC helped build the capacity of NGOs in three ways:
- Provided technical assistance to NGOs to support their ability to implement effective community-based programs in all health sector areas, including community-based family planning (CBFP).
- Supported procurement reform by giving grants to NGOs that carried out community-based activities.
- Built the capacity of NGOs to initiate or expand these services.
These support functions were used individually or in any combination. APC addressed all health sector areas including family planning; HIV&AIDS; maternal, newborn, and child health; nutrition; and control of infectious diseases.
APC's Community Health Systems Catalog is an innovative and interactive online tool that provides information about the community health systems of countries as well as countries with a strong interest in community-based family planning, a focus of the APC project. The Catalog provides information on the structure, management, staffing, and services included in the community health systems of each country. The information presented is based on individual country policies regarding the structure and implementation of the community health system.
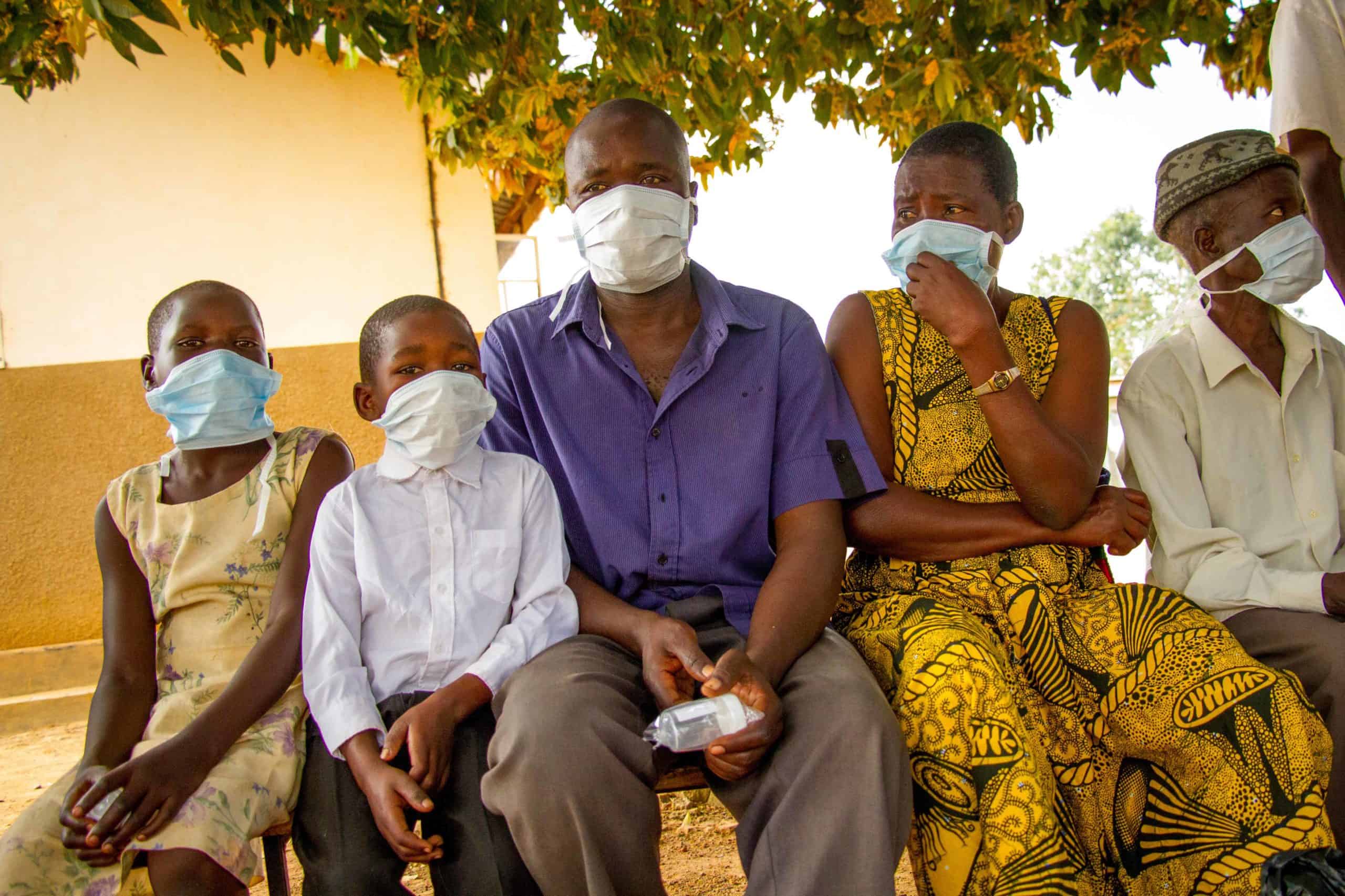
Following the 2014–2016 Ebola outbreak in West Africa, APC helped the governments in Guinea, Liberia, and Sierra Leone rebuild their health systems. The support focused on prevention of future outbreaks, systems recovery and resiliency, support to survivors, and improving health facilities. In Sierra Leone and Liberia, APC worked with ministries of health to shape and promote national policies that support services for Ebola irus disease (EVD) survivors as well as the general population. In Liberia, APC contracted two faith-based hospitals to provide comprehensive clinical care services for EVD survivors and helped 38 nurses and other mid-level health workers become mental health clinicians through a six-month training program.
APC was designed with a broad mandate so that it can contribute to GHI (gender, integration within and across sectors, partnerships with other donors and the private sector, health sector strengthening, country ownership, improved metrics, and identification of innovative and successful approaches). This project supports countries' journey to self-reliance by providing more direct grants to in-country partners. USAID Missions can use APC to give grants to local NGOs if they do not have sufficient capacity to directly oversee grants programs. Missions can also work with APC to give grants to NGOs that do not yet meet USAID eligibility criteria and help them bridge that gap.