Supportive Supervision to Improve Service Delivery
March 15th, 2021 | viewpoint
Supportive supervision, which incorporates self-assessment, peer assessment, and community input, advances quality improvement by strengthening communication, problem-solving, and teamwork, and preparing health providers to monitor and improve their performance.
In partnering with the Ethiopian Ministry of Health (MOH), regional health bureaus (RHBs), and federal agencies in the health sector, the USAID Ethiopia Digital Health Activity DHA uses a supportive supervision (SS) approach to deploy new technologies, provide maintenance support for existing tools, and revitalize performance review teams to use evidence-based decision-making. The Activity also uses SS to monitor the health sector’s progress toward product ownership and the use of data for decision-making.
The primary objectives of DHA’s use of SS are to identify elements of the health information system (HIS) in need of support and to address gaps at the grassroots level. The use of digitized tools helps to improve the quality of service at service delivery points. To increase the efficiency and effectiveness of the Activity’s SS, the Activity’s implementation team digitized the national SS checklist to streamline the collection of supervision data and automate the relay of data to a central server for real-time analysis and visualization of results. For this process, the implementation team used Open Data Kit (ODK), an open-source Android app that replaces paper-based data gathering. ODK supports a wide range of question types and is designed to work well with and without network connectivity.
DHA’s use of ODK increases the validity and accuracy of the Activity’s supervision data; makes real-time data available, which can be used as a baseline for future comparisons; and provides immediate feedback to the field team via a real-time visualization dashboard. (See Figures 1 and 2 for snapshots of the dashboard as field officers use ODK to send health facility data to the server.) ODK also records geolocation data, which supports the national Master Facility Registry (a platform for collecting, storing, and sharing authoritative information on Ethiopian health facilities) and helps the Activity to plan for future similar DHA engagements.
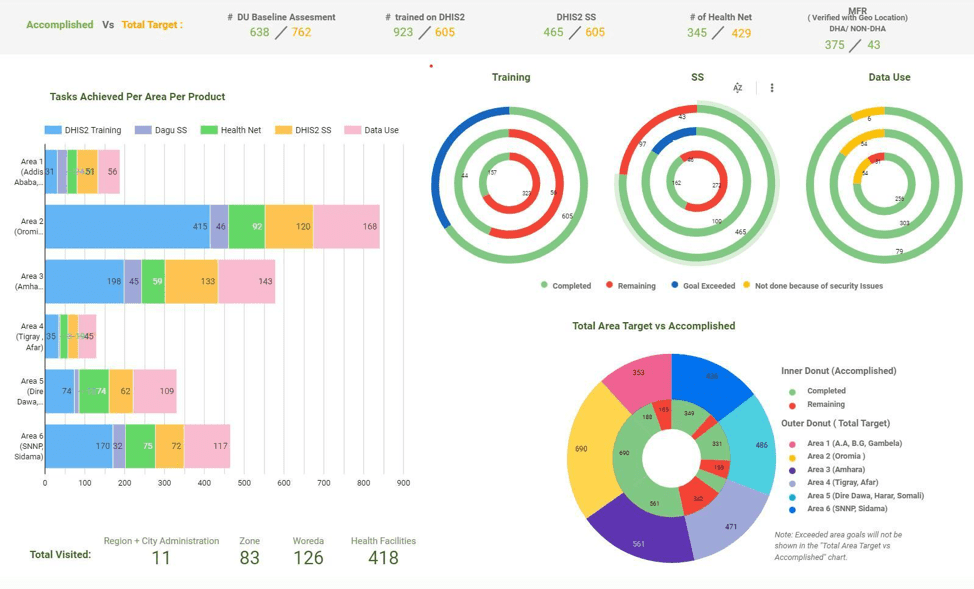
Figure 1. Snapshot of Field Activity Dashboard As Health Facility Data Are Sent to the Server Using ODK
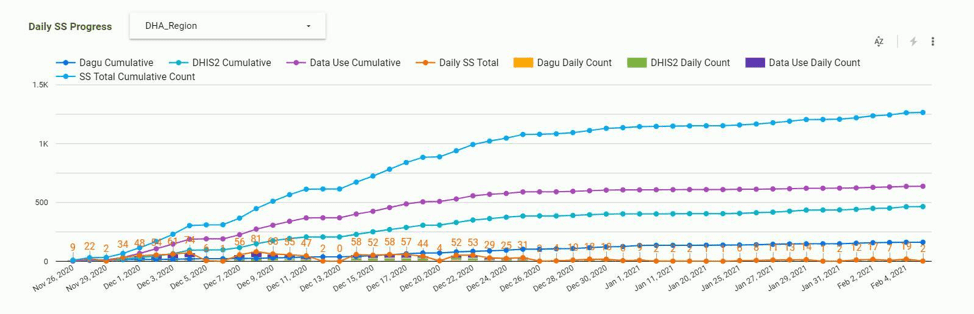
Figure 2. Snapshot of Field Supportive Supervision Activity Dashboard As Health Facility Data Are Sent to the Server Using ODK
We strive to build lasting relationships to produce better health outcomes for all.